Bioactive Nanofibrous Scaffolds Incorporating Decellularized Cell-Derived Extracellular Matrix for Periodontal Tissue Engineering
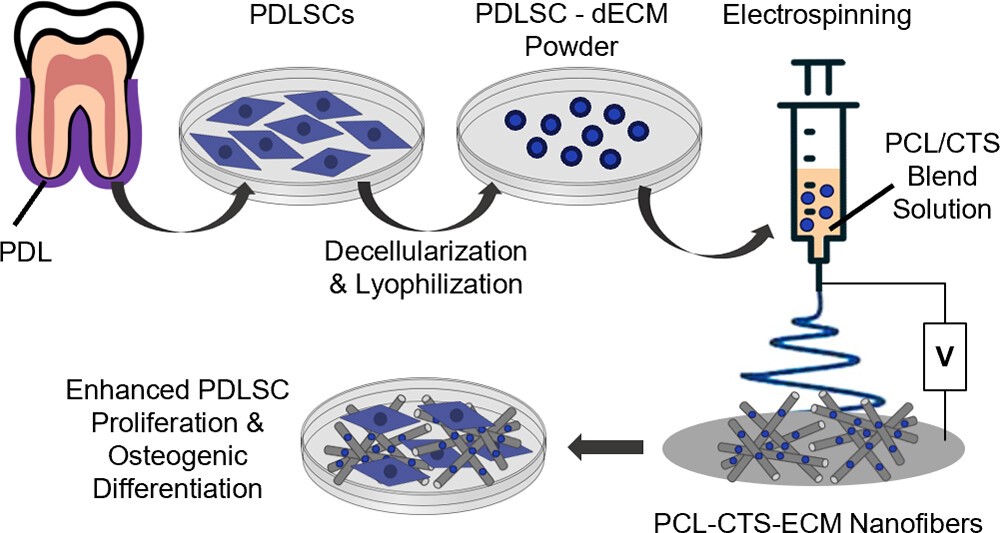
Current reconstructive treatments for periodontitis-related alveolar bone defects are based on the use of bone grafts with limited efficacy and predictability, lacking bioactive signals to induce tissue regeneration. Thus, tissue engineering strategies (TE) combining cell-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) with synthetic polymers to fabricate biomimetic scaffolds with proper mechanical properties and enhanced biofunctionality hold high promise to improve clinical outcomes. In a recent paper published in ACS Applied Nano Materials, SCERG-iBB researchers in collaboration with colleagues from CDRSP-Politécnico de Leiria developed bioactive cell-derived ECM-loaded electrospun polycaprolactone/chitosan (PCL/CTS) nanofibrous scaffolds by combining polymer solutions with lyophilized decellularized ECM derived from human periodontal ligament stem/stromal cells (hPDLSCs). The novel PCL/CTS/ECM scaffolds were characterized in terms of their structural, physicochemical, thermal, mechanical and in vitro biodegradation properties and were able to significantly improve the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs, proving their potential for periodontal TE strategies, particularly for alveolar bone regeneration.
Current reconstructive treatments for periodontitis-related alveolar bone defects are based on the use of bone grafts with limited efficacy and predictability, lacking bioactive signals to induce tissue regeneration. Thus, tissue engineering strategies (TE) combining cell-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) with synthetic polymers to fabricate biomimetic scaffolds with proper mechanical properties and enhanced biofunctionality hold high promise to improve clinical outcomes. In a recent paper published in ACS Applied Nano Materials, SCERG-iBB researchers in collaboration with colleagues from CDRSP-Politécnico de Leiria developed bioactive cell-derived ECM-loaded electrospun polycaprolactone/chitosan (PCL/CTS) nanofibrous scaffolds by combining polymer solutions with lyophilized decellularized ECM derived from human periodontal ligament stem/stromal cells (hPDLSCs). The novel PCL/CTS/ECM scaffolds were characterized in terms of their structural, physicochemical, thermal, mechanical and in vitro biodegradation properties and were able to significantly improve the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs, proving their potential for periodontal TE strategies, particularly for alveolar bone regeneration.
This study was developed under the scope of Mafalda Santos MSc thesis supervised by SCERG-iBB researchers Dr. João Silva and Dr. Marta Carvalho and was financially supported by the FCT project “DentalBioMatrix” (PTDC/BTM-MAT/3538/2020). See more.